how do they x ray babies hips
This image shows the. Think of the femoral head as the ball of the ball and socket joint.

How To Shower After Hip Replacement Surgery Hip Replacement Surgery Hip Replacement Exercises Hip Brace
Around 6 months of age enough bone is present in an infant hip to make an X-ray more accurate than ultrasound.

. This x-ray shows a dislocated hip on the patients right side. When babies are born they are examined to determine if their hips have formed normally. Begin by confirming the patients details reviewing the clinical history and checking the radiographs are of the correct anatomical site eg.
The American Academy of Pediatrics does not recommend routine ultrasounds for every infant. X-rays can be taken once your baby is 3 months old. Radiographers appear to like it.
Your baby will be placed on a table and positioned depending on which body area needs an x-ray. An x-ray can be done on any area of your babys body. It can occur bilaterally but it is usually asymmetric.
What will happen during the x-ray. Youll be asked to partly undress your baby and take off their diaper for the test. The maximum visual information is given by the x-ray of the hip joint in two projections.
The acetabulum is the socket. A hip X-ray is a safe and painless test that uses a small amount of radiation to make images of the hip joints where the legs attach to the pelvis. How Is Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Treated.
The femoral head should be seated deeply within the acetabulum. Hip ultrasounds are a safe non-invasive procedure that does not use any radiation. During the examination an X -.
Children use to grow and this means X-ray is done on baby bones and they will grow and growing tissue is altered by X-ray. Hip ultrasounds are a safe non-invasive procedure that does not use any radiation. Hip X-rays can be used to diagnose a disease monitor the progression of the disease determine a treatment.
They determined that modern x-rays have very low dose exposure and the total of two pelvis x-rays. In some children with cerebral palsy the femoral head can slowly begin to. After around 4 to 6 months of age X-rays are the preferred method for evaluating and monitoring hip dysplasia.
Your baby will be placed on a table on their back or side. It occurs more commonly in boys typically between 5 and 8 years of age but may range from the ages 3-12. In these younger children it is possible to nip the problem early with night time bracing to help the hips recover if hip dysplasia returns.
If a physical exam an ultrasound or an X-ray confirm a diagnosis your pediatrician will likely refer you to a pediatric orthopedic specialist for continued care and treatment. The first thing to look at in a hip x-ray is the relationship between the femoral head and the acetabulum. How is hip dysplasia treated in babies.
The babys legs have differences in their lengths or appearances. After around 4 to 6 months of age X-rays are the preferred method for evaluating and monitoring hip dysplasia. The doctor hears or feels a hip click when moving the infants thigh outward during a routine checkup.
A hip click can be felt by the examiner when the hip joints may not have formed normally. The X-ray can help a physician find a cause for the problems occurring. The rest of your babys body will be covered to protect him or her from the x-ray beam.
Perthes disease also known as Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is an idiopathic avascular necrosis of the proximal femoral epiphysis. In Alaska I had like 5-10 infant chest X-rays a day and that thing made my job 100 percent easier. A hip X-ray is used to view that area of the body where a patient is experiencing pain swelling or other abnormalities that require an internal view of the organs.
Im a nurse in a pedi operating room and Ive done them many times The hip dysplasia usually resolves on its own with the casting or bracing as the baby gets older. After around 4 to 6 months of age X-rays are the preferred method for evaluating and monitoring hip dysplasia. The scan usually takes about 20 minutes.
1 Two tests are performed called the Barlow and Ortolani tests to examine the function of the hip joints. Then a surgeon gently pushes the ball of their thighbone joint into the hip socket where it belongs. Its a cast that goes around both hips and down the leg to keep the hips aligned.
The authors of the second paper also evaluated the amount of x-ray exposure during follow-up evaluation. But for babies with an abnormal physical exam or major risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip or DDH family history Breech position etc the AAP supports referral for. Usually both hips are scanned.
Most children do not need surgery but for those who do an arthrogram x-ray dye injected into the hip joint at the beginning of the surgery can help the surgeon decide exactly what needs to be corrected. It is put on by an orthopedic surgeon while using x-ray to make sure the hip is aligned correctly. When interpreting a hip X-ray remember the following key points.
Ultrasounds use inaudible sound waves which bounce off of the bones and muscles to create an image for radiologists to interpret. Hip ultrasounds take less than 20 minutes and the child will not feel any pain during the examination. The doctor hears or feels a hip click when moving the infants thigh outward during a routine checkup.
You will go in the room with him he will need to be stripped from the waist down they will take x-rays of him flat on his back legs dead straight and together you wil be able to hold him in this position then an x-ray of his still on his back with his knees bent facing outwards and the soles of his. You may need to leave the room while the pictures are taken. As the baby grows the space between the bones slowly closes up.
Appointments and Referrals. Those things work great one person wrote on Reddit. During the examination an X-ray machine sends a beam of radiation through the pelvic bones and hip joints and an image is recorded on a computer or special film.
Totaleclipse 07092007 1731. In the direct projection or frontal obtained by focusing the x-ray tube perpendicular to the body plane - front or rear and axial transverse or horizontal plane fixing the elements of the joint from top to bottom - along the femur. Compare the images to previous radiographs where possible to provide additional context.

Uk Professor Says Swaddling Epidemic Gives Babies Clicky Hips Daily Mail Online Hips Professor Baby Swaddle

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Ddh Diagnostic Imaging Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Diagnostic Imaging Case Study

Hip Dysplasia In Adolescents And Young Adults Hip Dysplasia Young Adult Hip Problems

X Ray Image Of Child Swallowed The Coins For A Medical Diagnosis Medicine Pictures Children Images X Ray Images

Degenerative Joint Disease Frog Leg Hip Radiograph Shows Superolateral Joint Space Narrowing Sclerosis Subchondral Cyst A Radiography Osteophyte Radiology

Pin By Meg Carter On Ortho Hip Dysplasia X Ray Orthopedics

Anatomy Pathology Medicine Nursing Radiography Radiologictechnologist Radiology Radiologystudent Instagram Medical Anatomy Radiology Student Radiology

Karenhealey Amazing X Ray Radiology Diagnostic Imaging

Hip Dysplasia When You Re Too Young For A Hip Replacement Periacetabular Osteotomy Pao Hip Replacement Recovery Hip Replacement Hip Replacement Surgery

Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hips Start Screening For This At Age 2 Weeks With Barlow Nursing School Tips Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Nursery Nurse
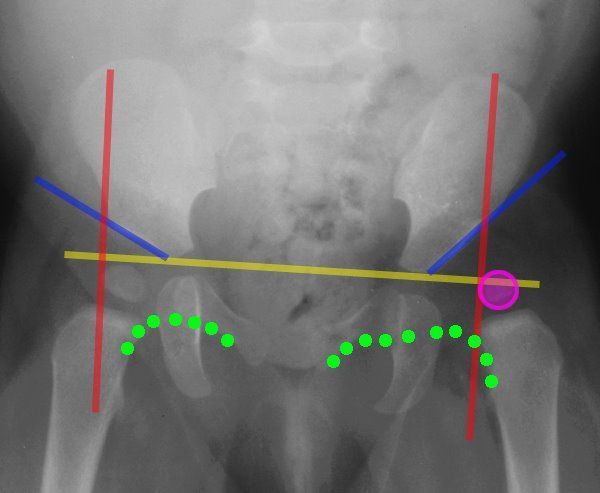
Lines Of The Hip Pediatrics Pediatrics Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Radiology

Hip Elbow Dysplasia Genetic Or Environmental Things To Ponder Hip Dysplasia Hips Dog Medicine

Congenital Hip Dislocation Chd Happens When A Child Is Born With An Unstable Hip Read On To Learn More Ab Canine Hip Dysplasia Hip Dysplasia Hip Dislocation

One Month Post Op From A Right Periacetabular Osteotomy To Correct Hip Dysplasia Ehlers Danlos Syndrome Surgery Recovery Hip Dysplasia




